Structured Query Language (SQL) is a fundamental tool for database management systems. Whether you’re a developer, data analyst, or database administrator, mastering SQL statements is essential for efficiently storing, retrieving, and manipulating data.
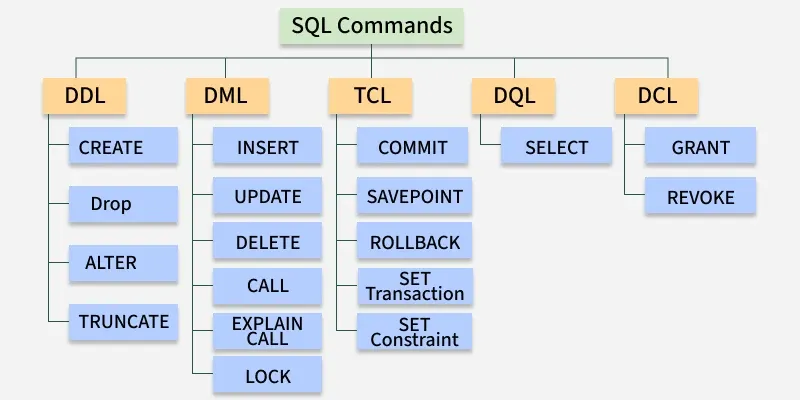
SQL statements are broadly classified into five categories, each serving a distinct role in database operations. Below, we’ll break down each category with practical examples to enhance your understanding.
1. Data Definition Language (DDL)
DDL statements define and modify the structure of database objects like tables, schemas, and indexes.
Common DDL Commands:
- CREATE – Create new database objects (tables, views, schemas, etc.)
- ALTER – Modify existing database objects
- DROP – Remove objects from the database
- TRUNCATE – Quickly delete all records from a table
Examples:
-- Create a new table
CREATE TABLE Employees (
EmployeeID INT PRIMARY KEY,
FirstName VARCHAR(50),
LastName VARCHAR(50),
Department VARCHAR(50),
Salary DECIMAL(10,2)
);
-- Add a new column to an existing table
ALTER TABLE Employees ADD Email VARCHAR(100);
-- Remove a column
ALTER TABLE Employees DROP COLUMN Department;
-- Delete the table permanently
DROP TABLE Employees;
2. Data Manipulation Language (DML)
DML statements are used to manage data within tables.
Common DML Commands:
- INSERT – Add new records
- UPDATE – Change existing records
- DELETE – Remove records
Examples:
-- Insert a new record
INSERT INTO Employees (EmployeeID, FirstName, LastName, Salary)VALUES (1, 'John', 'Doe', 50000);
-- Update the salary for a specific employee
UPDATE Employees SET Salary = 55000 WHERE EmployeeID = 1;
-- Delete a record
DELETE FROM Employees WHERE EmployeeID = 1;
3. Data Query Language (DQL)
DQL primarily revolves around the SELECT statement, which is used to fetch data from tables.
Examples:
-- Retrieve all records
SELECT * FROM Employees;
-- Retrieve specific columns
SELECT FirstName, LastName, Salary FROM Employees;
-- Apply conditions
SELECT * FROM Employees WHERE Salary > 60000;
-- Use aggregate functions
SELECT Department, AVG(Salary) AS AverageSalary FROM Employees GROUP BY Department;
4. Data Control Language (DCL)
DCL statements manage access rights and permissions within the database.
Common DCL Commands:
- GRANT – Give user access privileges
- REVOKE – Remove user access privileges
Examples:
-- Grant SELECT access on Employees table to a user
GRANT SELECT ON Employees TO 'dbuser';
-- Revoke access
REVOKE SELECT ON Employees FROM 'dbuser';
5. Transaction Control Language (TCL)
TCL commands are used to control transactions and maintain data integrity.
Common TCL Commands:
- COMMIT – Save all changes made in a transaction
- ROLLBACK – Undo changes if an error occurs
- SAVEPOINT – Set a point to which a transaction can be rolled back
Examples:
-- Start a transaction
BEGIN;
-- Insert a new employee
INSERT INTO Employees (EmployeeID, FirstName, LastName, Salary)VALUES (2, 'Jane', 'Smith', 60000);
-- Commit the transaction if successful
COMMIT;
-- Roll back the transaction if needed
ROLLBACK;
Conclusion
SQL statements are essential for successful database management. Each category—from defining structures (DDL) to managing transactions (TCL)—plays a vital role. By comprehending and applying these SQL statement types, you can effectively work with relational databases and develop robust, data-driven applications.