Azure Data Factory (ADF) is Microsoft’s cloud-based platform for ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) and data integration. Two fundamental components—Linked Services and Datasets in ADF—enable ADF to connect to external systems and process data efficiently.
This guide provides a clear walkthrough to create Linked Services and Datasets in ADF:
- What Linked Services and Datasets are
- How to create Linked Services in ADF
- How to create Datasets in ADF
- Step-by-step instructions for each process
1. Understanding Linked Services and Datasets in ADF
Linked Services:
Think of these as the connection details or credentials ADF uses to connect to external resources such as Azure Blob Storage, Azure SQL Database, or on-premises data sources.
Datasets:
Datasets define what data within those connections is being used—such as a specific file, folder, or database table.
In summary:
- Linked Service: Specifies where the data is stored
- Dataset: Specifies what data to use from that location
2. Creating a Linked Service in ADF
Step 1: Open Azure Data Factory Studio
- Log in to the Azure Portal.
- Navigate to your Data Factory resource.
- Click on Launch Studio to open ADF Studio.
Step 2: Add a New Linked Service
- In ADF Studio, go to the Manage tab (gear icon on the left panel).
- Select Linked Services.
- Click + New.
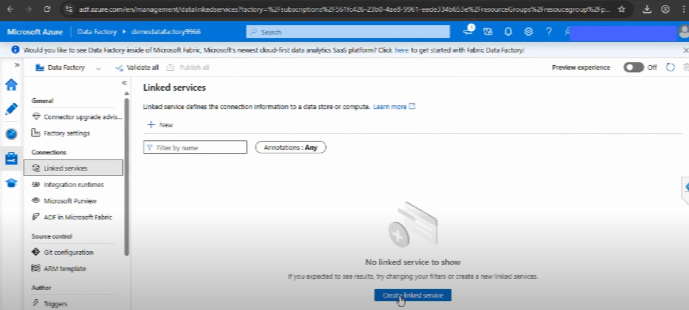
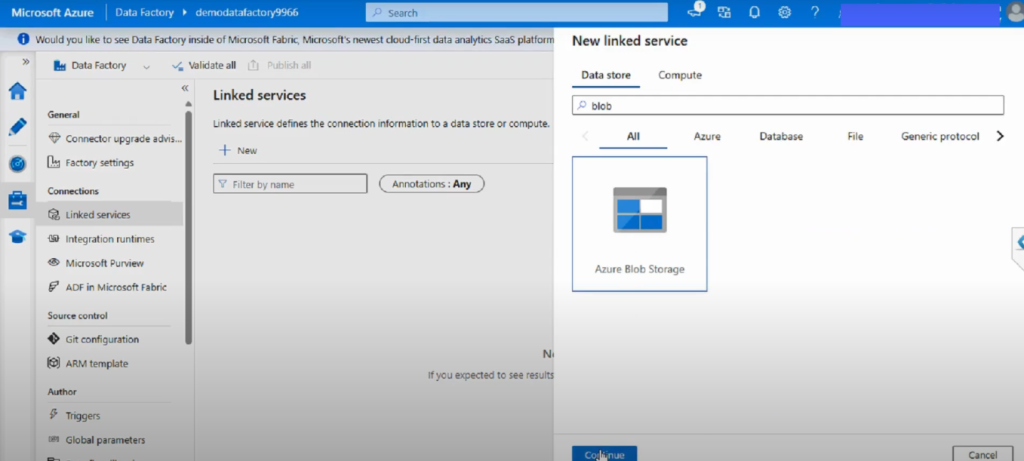
Step 3: Choose a Data Source
- Browse the list of supported connectors (Azure Blob Storage, Azure SQL Database, Salesforce, Amazon S3, etc.).
- Select your desired data source (e.g., Azure Blob Storage).
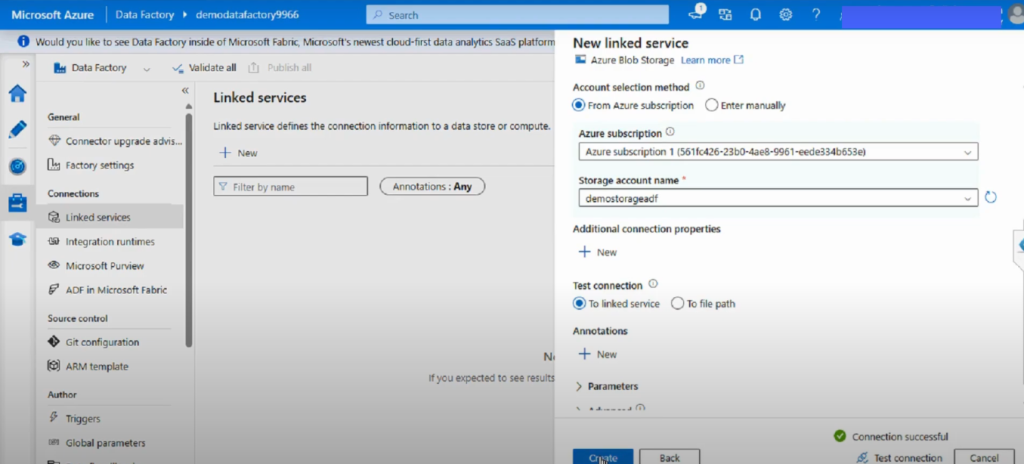
Step 4: Configure the Connection
- Enter required details: Name, Subscription, Storage Account.
- Choose an authentication method (Account Key, Managed Identity, or Service Principal).
- Test the connection.
- Click Create.
Your Linked Service is now set up!
3. Creating a Dataset in ADF
Step 1: Go to the Author Section
- In ADF Studio, open the Author tab (pencil icon).
- Click + and select Dataset.
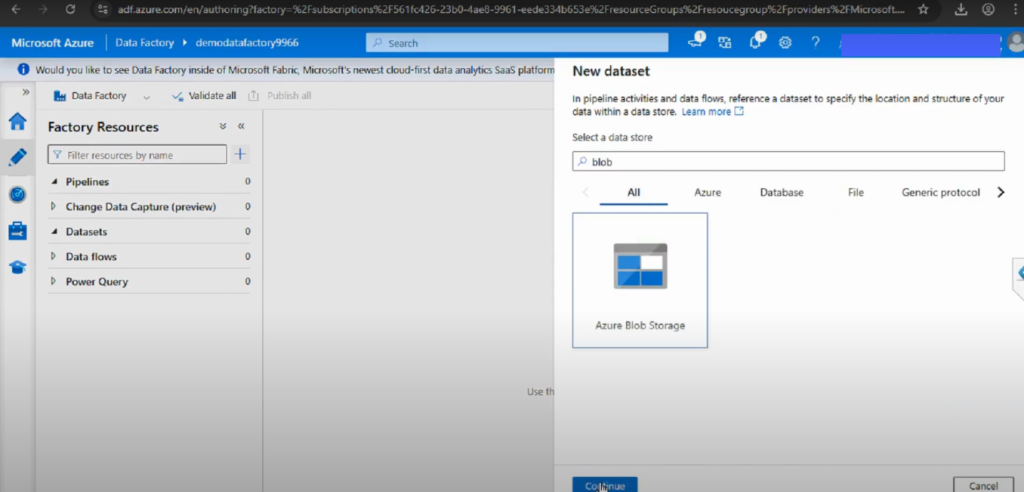
Step 2: Select Data Store Type
- Choose the dataset type.
- For example, select Azure Blob Storage → DelimitedText for CSV files.
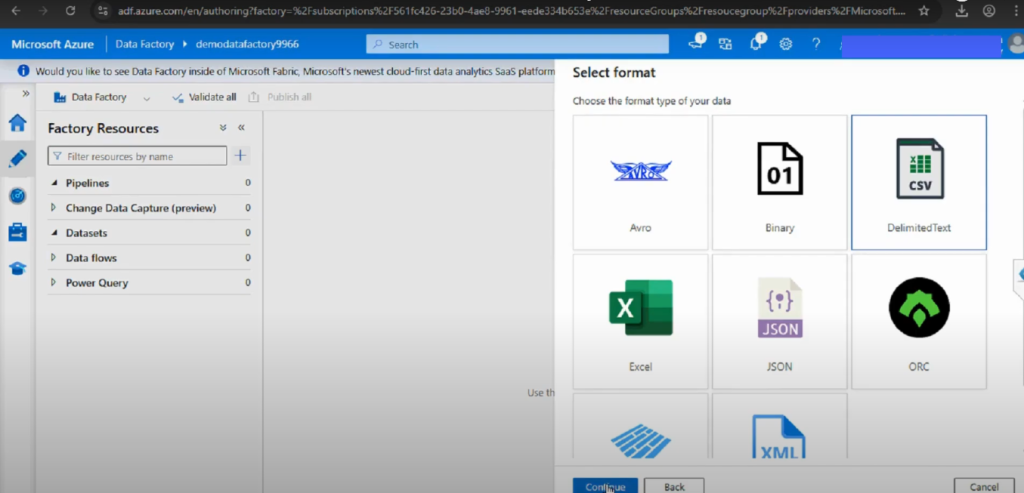
Step 3: Configure the Dataset
- Provide a name for the dataset.
- Select the Linked Service you created earlier.
- Browse to select the container, folder, or file path.
- Check the option for ‘First row as header’ if working with CSVs.
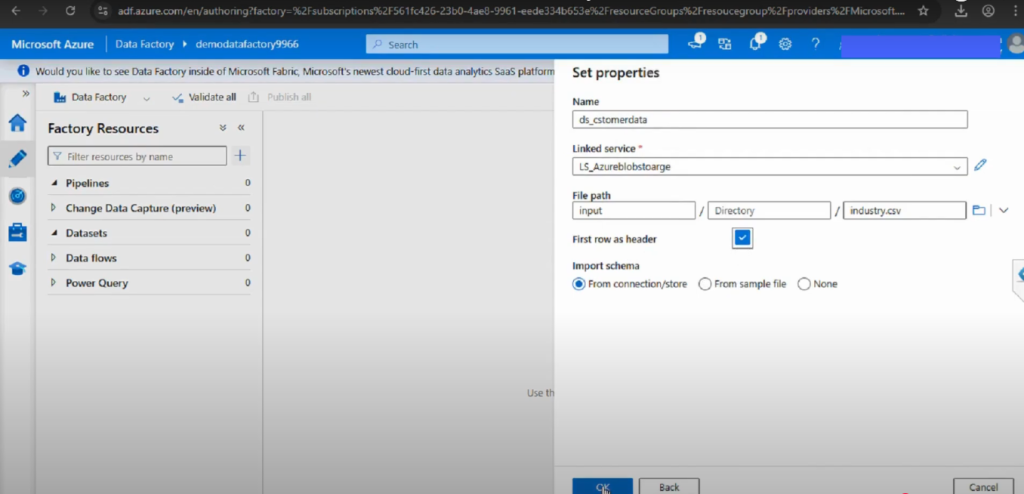
Step 4: Save and Publish
- Click OK to save the dataset.
- Click Publish All (top menu) to apply your changes.
4. Example: Moving Data from Blob to SQL
- Linked Service 1: Azure Blob Storage (source)
- Linked Service 2: Azure SQL Database (destination)
- Dataset 1: Blob dataset for a CSV file
- Dataset 2: SQL dataset for a target table
This configuration enables you to transfer data from Azure Blob Storage to Azure SQL Database using an ADF pipeline.
5. Best Practices
- Use Managed Identity for authentication when possible.
- Follow clear naming conventions (e.g., LS_Blob_Storage, DS_Sales_CSV).
- Always validate and test connections before publishing.
- Organize datasets with folders in large projects.
6. Common Issues and Troubleshooting
- Connection Test Failed
- Check firewall settings in SQL or Storage.
- Ensure the correct authentication method is used.
- Dataset Schema Errors
- Re-import schema if file format changes.
- Use schema drift (wildcard) for semi-structured data.
Conclusion
Setting up Linked Services and Datasets in ADF is an essential step in building scalable, reliable data integration pipelines. By defining where your data is and what data you need, you enable ADF to orchestrate complex workflows with ease.
These components act as the foundation for everything else you do in Data Factory. Without well-structured Linked Services and properly designed Datasets, pipelines can quickly become difficult to manage. By following best practices such as using Managed Identity for authentication, parameterizing datasets for reusability, and adopting consistent naming conventions, you’ll ensure that your data integration environment remains secure, flexible, and maintainable.
With these steps in place, you’re ready to move on to pipeline creation and data transformation in ADF.
📌 Watch the full video here: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=IXGBH6VluZQ